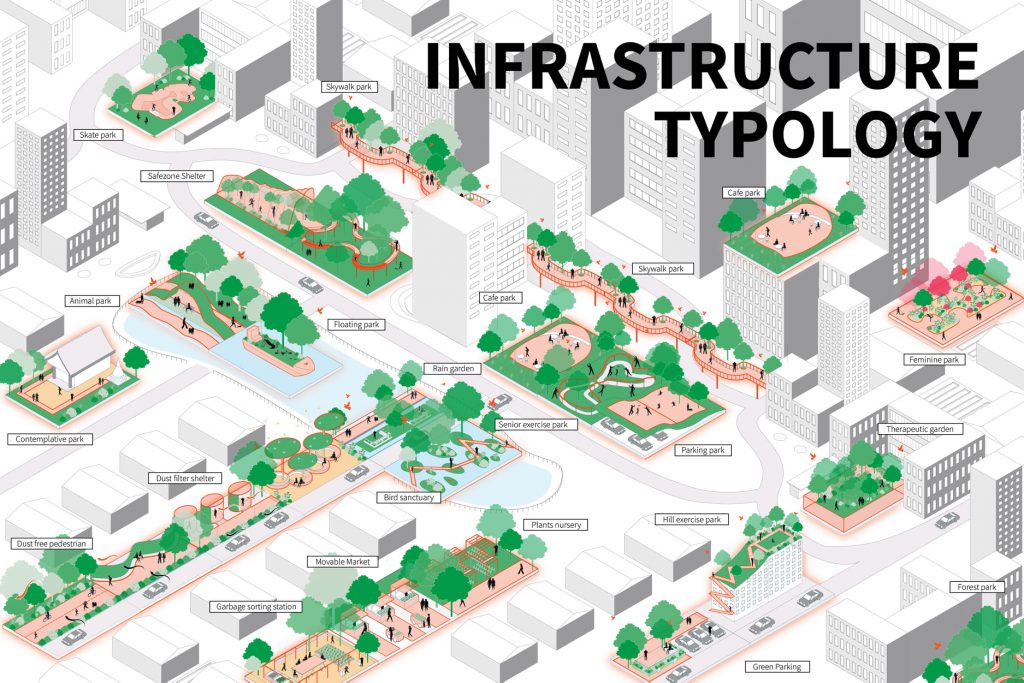
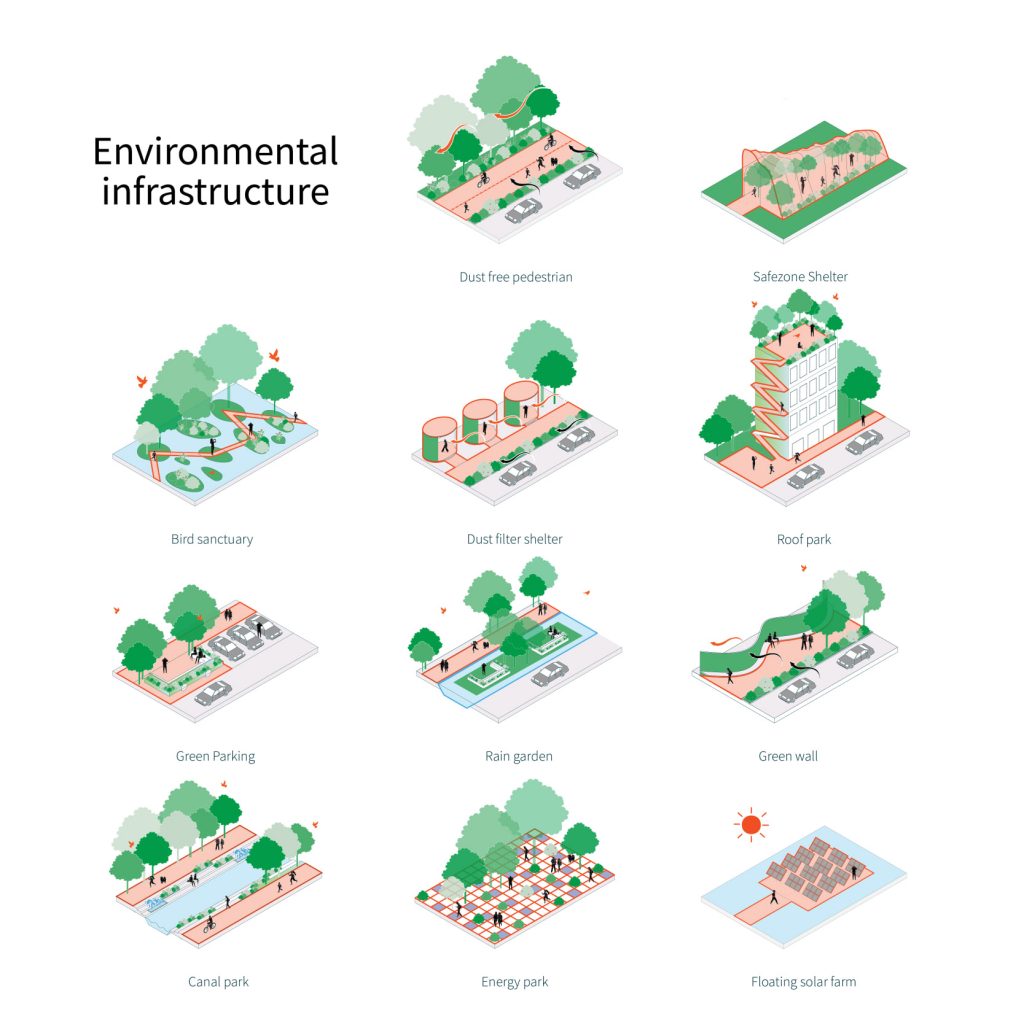
Green Environmental Infrastructures
‘Green Environmental Infrastructures’ focuses on tackling environmental problems such as pollution, urban heat, and flood. For example, greens that are located on the sidewalks help absorb pollution from transport and generate a pleasant atmosphere for pedestrians when walking in the city. Green walls help relieve urban heat and cools down the building temperature resulting in less energy consumption. Making the impact of emissions less severe. These two typologies are not the only methods green spaces can help mitigate environmental issues, but there are much more we can do to contribute to the cause such as cooperating these spaces into the cities: safe zone and dust-filter shelters, bird sanctuaries, roof parks, green parking, rain gardens, canal and energy parks, or floating solar farms.
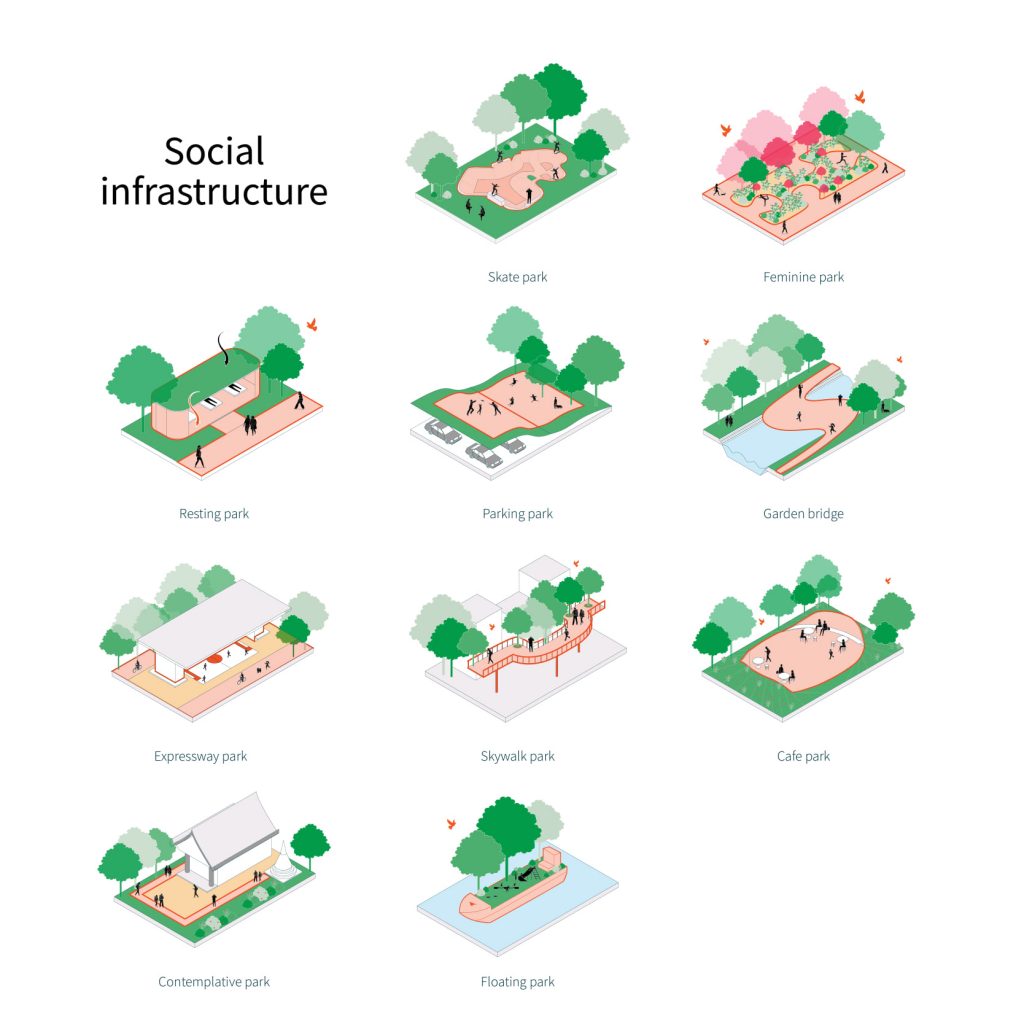
Social Infrastructures
‘Social Infrastructures’ prioritizes creating socializing spaces along with embedding greens into them. Existing infrastructures like parking lots, skating rinks, or expressway stops do not include greens into the design as much as they could. A lot of these spaces miss out on the opportunity to help create a sustainable environment. Although these places do not have lots of spaces, if these small patches of greenery are combined together, it can make a difference.
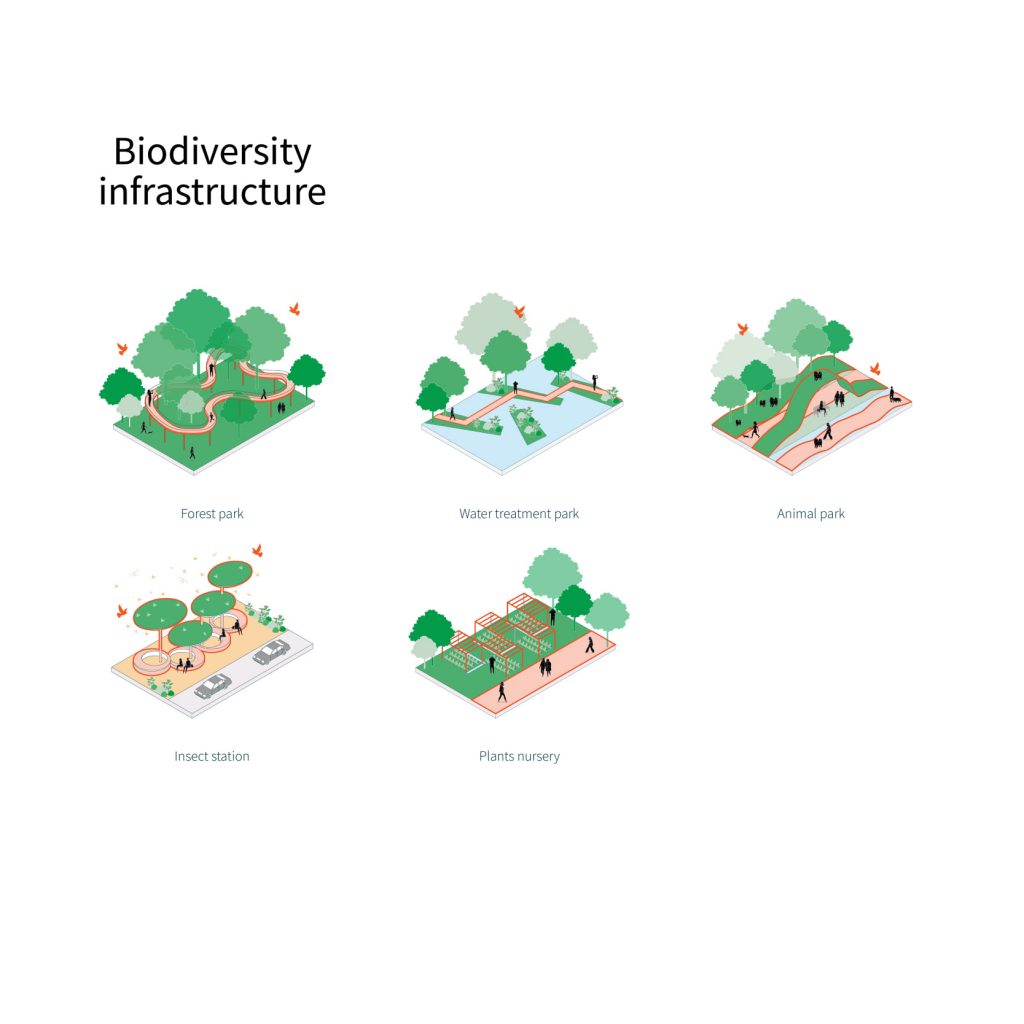
Biodiversity Infrastructure
Biodiversity Infrastructure’s purpose is to help restore back sustainability, we need to realize that we are not the only creatures in this world. We should be attentive towards plants and other wildlife. Developing forest, water treatment, and animal parks, as well as insect stations or plants nursery, is one way we can maintain the biodiversity of nature. Biodiversity Infrastructures not only offers possible solutions to humans, but to nature as well.

Food Infrastructure
Food Infrastructure deals with the issue of food security. As the world population increases, our resources become even more scarce and limited. Food infrastructure is one method that helps ensure that spaces will not be wasted, and promotes community participation through places like, urban farms, movable markets, garbage sorting stations, or canal gardens.
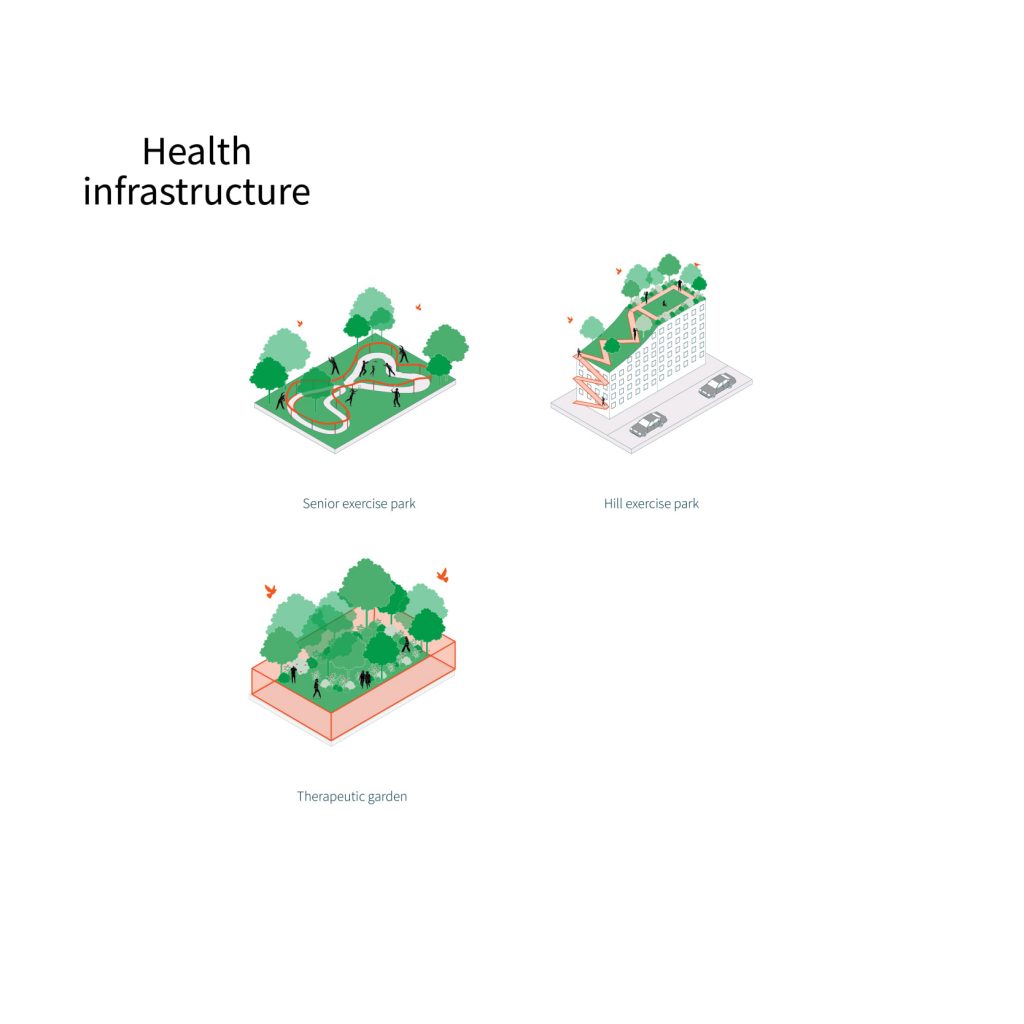
Health Infrastructure
‘Health Infrastructures’ emphasizes on improving the well-being of urban dwellers. These infrastructures cater to various age groups considering their capabilities and interests. Not only does it ameliorate one’s physical conditions, but as well as one’s mental needs such as a therapeutic garden that helps relieve stress with the presence of trees and nature. While senior exercise parks and hill exercise parks encourage physical activities with proper facilities.

